Components
Input
Input fields are essential UI elements that allow users to enter non-standardized responses, commonly seen in e-commerce forms and online queries.
Components
Input fields are essential UI elements that allow users to enter non-standardized responses, commonly seen in e-commerce forms and online queries.
 Free
Free
8 Variants
 Free
Free
16 Variants
96 Variants
 Free
Free
1128 Variants
 Free
Free
36 Variants
 Free
Free
340 Variants

336 Variants
 Free
Free
960 Variants

86 Variants
70 Variants
 Free
Free
128 Variants
 Free
Free
100 Variants
 Free
Free
2404 Variants
 Free
Free
16 Variants
 Free
Free
256 Variants
 Free
Free
12 Variants
 Free
Free
20 Variants
 Free
Free
50 Variants
 Free
Free
896 Variants
196 Variants
 Free
Free
784 Variants
 Free
Free
840 Variants

149 Variants

22 Variants
 Free
Free
50 Variants
 Free
Free
1792 Variants
 Free
Free
64 Variants

6 Variants
256 Variants
 Free
Free
64 Variants
580 Variants
 Free
Free
144 Variants

36 Variants

7 Variants

441 Variants

8 Variants
 Free
Free
14 Variants
 Free
Free
12 Variants

16 Variants

32 Variants
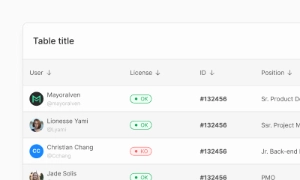
The Input component in Emvi UI is a versatile UI element designed for user data entry while maintaining visual consistency across Figma prototypes and production code via Tailwind. Ideal for text inputs, search fields, forms, and interactive UIs, it adapts seamlessly to both free and premium versions of Emvi UI. It prioritizes clarity, accessibility (WCAG-compliant), and usability in various states (default, focus, filled, error, disabled). Through design tokens (e.g., input.bg, input.border, input.focus, input.error), Emvi UI ensures consistent implementation across platforms.
Input fields are vital for collecting user information in various contexts. Whether entering personal details, delivery addresses, or sending queries, these fields provide a flexible way for users to submit their responses. They are a key component in forms, making it possible to gather unique and specific information from each user.
Input fields are highly versatile and can be used in many different situations. From login forms and search bars to feedback forms and comment sections, input fields adapt to the needs of the application. They can handle text, numbers, passwords, emails, and more, ensuring that all types of data can be accurately captured and processed.
Input fields enhance the user experience by making data entry straightforward and efficient. Clear labels, placeholder text, and proper field alignment guide users through the process, reducing errors and frustration. In e-commerce, for instance, well-designed input fields ensure that users can quickly and easily complete their purchases. Our UI kit includes customizable input field components that can be tailored to fit any design, providing a seamless and user-friendly interface.
Outlined: clean border-focused style for minimalist layouts
Filled: subtle background fill for emphasis or elevated surfaces
With Icon: optional leading or trailing icon (search, clear)
Multiline (textarea): for extended user input
Disabled: non-editable state visually muted
Responsive variants: available for both light and dark themes.
SM: compact forms, dense UIs
MD: default, balance between space and readability
LG: onboarding or touch-driven contexts
Maintain consistent heights (matching primary buttons) and uniform widths. Figma Auto Layout ensures proper alignment; Tailwind uses h-10, px-3, gap-2, etc., for spacing. Touch areas meet ≥44×44 px guidelines.
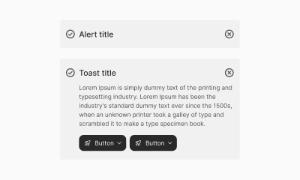
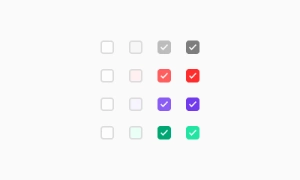
Default / Focus / Filled / Hover / Disabled / Error
Transitions and visual feedback ensure clarity (e.g., focus ring, border highlight)
Auto layout and proper label placement prevent misalignment in dynamic forms
Masks and validation indicators improve input accuracy and UX (e.g., phone, date)
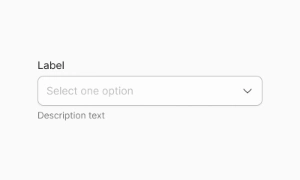
Labels always visible and descriptive (avoid placeholder-only labels)
High contrast for text, borders, and background
Clear differentiation of required vs optional fields
Error messages placed below or to the right of the input and linked via ARIA (aria-describedby)
Keyboard focus use focus-visible style
Figma: Variants for default, focus, filled, disabled, error
Icon slots configurable in component variants
Auto Layout for vertical/horizontal alignment
Style tokens for text, border, fill, focus
Tailwind: Layout: block w-full rounded-md border
States: focus:border-primary-500, focus:ring, disabled:bg-neutral-100
Responsive: sm:h-8, lg:px-4
Tokens: input.border, input.focus, input.bg
Keep forms concise—minimize visible fields
Use explicit labels (top-aligned preferred for speed)
Place error messages below or right of inputs for clarity
Don't use placeholders as sole label context
Apply localized input masks for formatted data
Maintain consistent input/button heights for rhythm